Kalesar National Park, District Yamunanagar
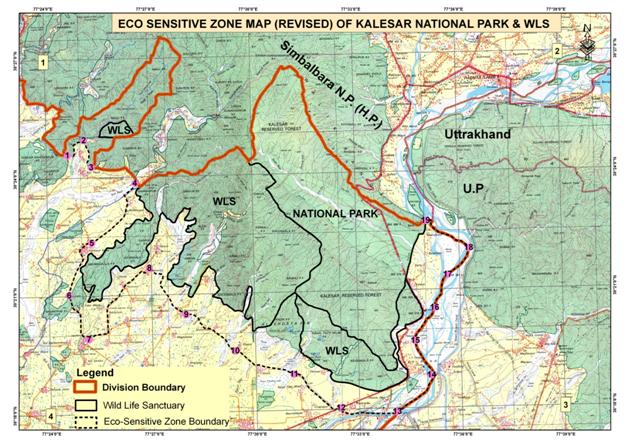
Kalesar National Park is situated in the foot hills of Shiwalik ranges of mighty Himalayas. On map it is located between 300 18’ to 300 27’ North latitude & 770 18’ to 770 35’ East longitude. It falls under Yamunanagar District of Haryana, sharing boundary with three States viz., Himachal Pradesh, Uttranchal & U.P. The Yamuna river form the Eastern boundary with Uttar Pradesh, the main Shiwalik ridge separates State boundary among Haryana, Himachal Pradesh & Uttaranchal in the north.
Kalesar National Park is named after the Kalesar (shiva) temple located in protected area. The whole area is full of bio-diversity having dense Sal forests, Khair forests and patches of grass lands, which support an amazing variety of plants and animal species.
The park was declared as National Park on 8th December 2003 having an area of 11570 acres. Just adjacent to the National Park is Kalesar Wildlife Sanctuary and it was notified on 13th December 1996, having an area of 13209 acres.
Statement of Significance
 Kalesar National Park has got lot of significance in terms of bio-diversity and ecological stability in this part of the country. In terms of bio-diversity, it is store house of numerous medicinal plants. It houses many threatened animals like Leopard, Ghoral, Barking deer, Sambar, Chital, Python, King Cobra, Monitor lizard etc. Occasionally, Tigers and Elephants visit this park from Rajaji National Park situated in Uttranchal. If little improvement in habitat management is done in this park, tigers and elephants may stay throughout the year. So this park is very important in conservation of highly threatened animals like tiger and elephant. This habitat can provide alternate home for these two animals coming from Rajaji National Park.
Kalesar National Park has got lot of significance in terms of bio-diversity and ecological stability in this part of the country. In terms of bio-diversity, it is store house of numerous medicinal plants. It houses many threatened animals like Leopard, Ghoral, Barking deer, Sambar, Chital, Python, King Cobra, Monitor lizard etc. Occasionally, Tigers and Elephants visit this park from Rajaji National Park situated in Uttranchal. If little improvement in habitat management is done in this park, tigers and elephants may stay throughout the year. So this park is very important in conservation of highly threatened animals like tiger and elephant. This habitat can provide alternate home for these two animals coming from Rajaji National Park.
The Shiwaliks formed by debris from the older Himalayan ranges, are composed of sedimentary rocks such as sand stone, clays & conglomerates & is a highly fragile system. Extensive erosion takes place due to rapid run off during heavy rains. Gullies and land slides are common and the valley bottoms and nallahs are mostly strewn with boulders and pebbles. During monsoon, torrents carry boulders & muddy water and cause flash floods in the plains. So this protected area plays vital role in preventing that kind of flash floods and helps in maintaining ecological stability. In Haryana, it is the only National Park having good natural forest supporting such a large bio-diversity. So it has got a special significance in terms of conservation, education, tourism and research opportunities.
Boundaries
The entire National Park & Sanctuary area is duly notified and demarcated on the ground with the help of pillars and natural boundaries like rivers and torrents. To the North of National Parks Simbalwada Wildlife Sanctuary (Himachal Pradesh) is located which is separated by ridge line and marked by pillers. To the East, Yamuna river makes boundary of park with Uttar Pradesh. To the South agriculture lands of villages viz., Tajewala, Araynwala, Naggal, Tiberian, Khizri, Baghpat, Khillanwala, Kansli, Darpur, Chicken, Jatanwal and Kot are situated. The western side is bounded by the crop fields of villages Faqirmajra and Ibrahimpur.
Animals
Corresponding to the considerable diversity of habitat types, the wild animals of Kalesar protected area show a good variety of species. Although numbers are rather low at present, due to the full protection provided by park authorities, the population will increase to the full carrying capacity of the area within few years. Among herbivores, Sambhar is common, especially in the more densely forested areas on gentle slopes, where groups of 2 to 4 are often seen. Chital is another common herbivore found in open grassy patches and fire lines. Barking deer is found especially in forest areas with ample ground cover. The Goral is found in the park occupying a specialized niche on the relatively bare rocky slope at the top of Shiwalik ridges.
Antelopes are represented by the Rojh (Blue Bull) bull which occurs in the more open areas bordering Yamuna plain. Wild boar is also fairly common in the park and it also raids on crops. Elephant is a occupational visitor from Rajaji National Park. Elephants use to stay at Kalesar Protected Area for few weeks and used to go back to Rajaji National Park. If good waterholes are made available, it may stay for longer duration.
The Rhesus macaque is most common monkey in the park and most of these were released in the park area from outside. Presently, their number is too high. These monkeys also feeds on eggs of Red Jungle fowl, so there is a apprehension that there is a decrease in Red Jungle Fowl number. Most of the time, these monkeys attack on villages and also go for crop raids. Among the carnivores in Kalesar protected Area, leopard take pride place. There are about 20-22 leopard in the entire Protected Area. The tiger is also an occasional visitor from Rajaji national park. It stays for few days and goes back. If there is increase in prey base, it can permanently stay in the park.
Safari Arrangement in the National Park
There is an arrangement to take up safari visit in the National Park area by a hired Geep. For this purpose, Wildlife Wing of Forest Department has granted permission to local persons who can be contacted for this purpose through Wildlife Inspector, stationed at Kalesar National Park. The hiring charges shall be payable to the Geep owner as per the existing hiring charges prevalent in the area.
Safari Routes in the Park
For the purpose of facilitating the visitors for taking up safari in the park area, three safari routes have been delineated in the National Park. These routes are fully motor able with the total motor able length of approximately 16 kms. These routes are as under:-
- Route No. I. 20 feet wide motorable road with length of 7.0 kms.
- Route No. II. 60 feet wide motorable road with length of 6.5 kms.
- Route No. III. 60 feet wide motorable road with length of 6.0 kms.
It may be noted that only those private Geeps are permitted to enter into the National Park area which are registered with office of Wildlife Inspector, Kalesar having permission of entry.
The timings of visiting National Park
The following are the timings for summer and winter months:-
Summer months
- 06:00 AM to 10:00 AM
- 04:00 PM to 07:00 PM
Winter months
- 07:00 AM to 11:00 AM
- 03:30 PM to 06:00 PM
The best season for visiting the National Park during the year is in the month of November to December and March to June. The National Park remains closed in the months of July to September.
Contact Details
Phone: 094678 59568
Address: Yamuna Nagar, Haryana 135106
How to Reach
By Train
The nearest railway station is at Yamunanagar.
By Road
Yamunanagar Ponta Sahib State highway passes through the Kalesar National Park. It is around 45 Km from Yamunanagar, 15 Km from Ponta, and 55 Km from Dehradun. It is well connected by road and having good services from Yamunanagar and Ponta Sahib.

